Black-billed thrush
“The Black-billed thrush sings a sweet melody that echoes through the forest.”
Best Quotes for Black-billed thrush Bird
Black-billed thrush Lifespan related to Black-billed thrush Predators & Black-billed thrush Conservation Status also Black-billed thrush Location and Habitat important regarding Black-billed thrush Reproduction & Black-billed thrush Diet for Black-billed thrush Behavior of the Bird
Black-billed thrush Scientific Classification
Domain: Chordata
Kingdom: Aves
Phylum: Passeriformes
Class: Turdidae
Order: Turdus
Family:
Genus:
Species:
Data Source: Wikipedia.org
Black-billed thrush Characteristics
The Black-billed thrush is a small bird that is native to Central and South America. It is known for its distinctive black bill and dark plumage. These birds are typically found in forests and wooded areas, where they feed on insects, fruits, and berries. They are known for their beautiful songs, which they use to communicate with other birds and attract mates. The Black-billed thrush is an important part of the ecosystem, as they help control insect populations and spread seeds through their droppings.
Black-billed thrush Lifespan
The Black-billed thrush has an average lifespan of around 4 to 6 years. However, some individuals have been known to live up to 10 years in the wild. This bird species faces threats such as habitat loss and climate change, which can impact their lifespan.
Black-billed thrush Diet
The Black-billed thrush eats a variety of insects, fruits, and berries. They are known to forage on the ground for food, picking up insects and small fruits. They also eat worms, snails, and spiders as part of their diet.
Black-billed thrush Behavior
The Black-billed thrush is a shy bird that is often seen hopping on the ground in search of insects. It is known for its beautiful song and cautious demeanor.
Black-billed thrush Reproduction
Black-billed thrushes reproduce by building nests in trees and laying eggs. The female incubates the eggs while the male brings food. The chicks hatch and grow in the nest.
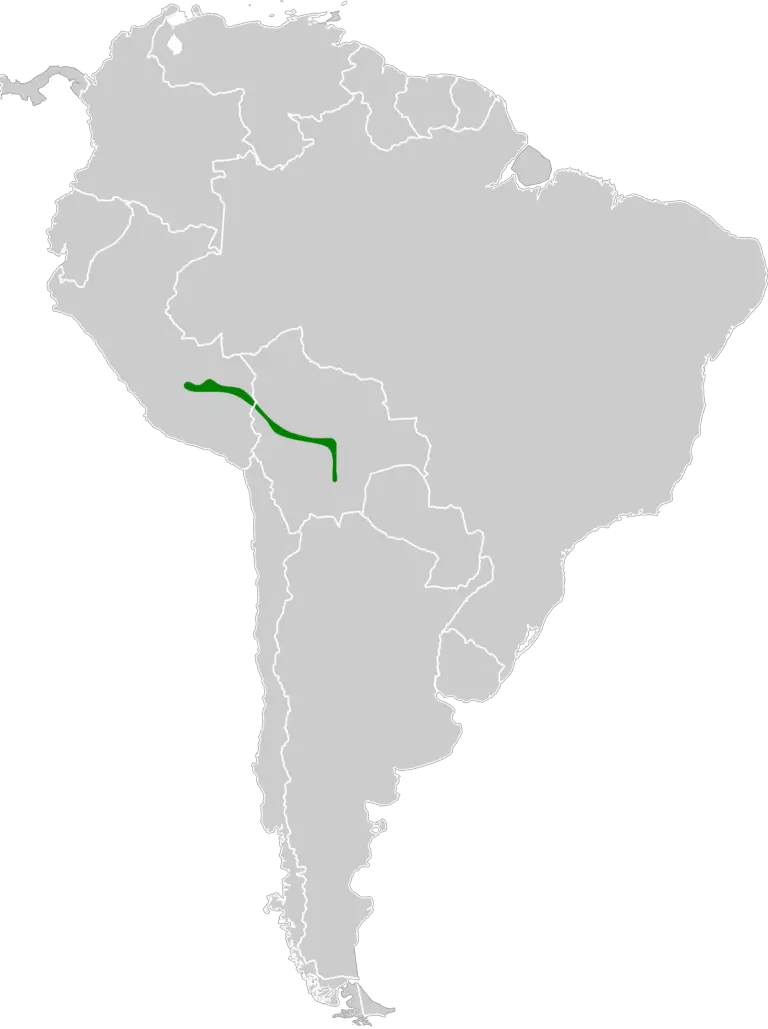
Black-billed thrush Location and Habitat
The Black-billed thrush can be found in the dense forests and woodlands of Central and South America. They prefer areas with thick vegetation and plenty of insects for food.
Black-billed thrush Conservation Status
The Black-billed thrush is listed as a species of “Least Concern” on the conservation status scale, meaning they are not currently at risk of extinction.
Black-billed thrush Predators
The Black-billed thrush faces threats from snakes, cats, and larger birds like hawks and owls. These predators hunt the thrush for food and pose a serious danger.
Black-billed thrush FAQs
- What is a Black-billed thrush?
A Black-billed thrush is a species of bird known for its distinctive black bill and brownish-black plumage. - Where can Black-billed thrushes be found?
Black-billed thrushes are native to Central and South America, primarily in countries like Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras. - What do Black-billed thrushes eat?
Black-billed thrushes primarily feed on insects, fruits, and berries found in their natural habitat. - How do Black-billed thrushes communicate?
Black-billed thrushes communicate through a series of melodic calls and songs. - Are Black-billed thrushes endangered?
Black-billed thrushes are not currently considered endangered, but their populations are declining due to habitat loss. - How big are Black-billed thrushes?
Black-billed thrushes are medium-sized birds, typically measuring around 8 to 9 inches in length. - Do Black-billed thrushes migrate?
Black-billed thrushes are known to migrate seasonally, moving to warmer climates during the winter months. - How do Black-billed thrushes build their nests?
Black-billed thrushes build cup-shaped nests using twigs, grass, and mud, typically placed in dense vegetation. - Do Black-billed thrushes have any predators?
Black-billed thrushes are preyed upon by birds of prey, snakes, and small mammals. - Can Black-billed thrushes mimic other bird species?
Black-billed thrushes are not known for their ability to mimic other bird species, unlike some other thrush species.