Black-headed bunting
“The vibrant colors of the Black-headed bunting never fail to captivate the eye.”
Best Quotes for Black-headed bunting Bird
Black-headed bunting Lifespan related to Black-headed bunting Predators & Black-headed bunting Conservation Status also Black-headed bunting Location and Habitat important regarding Black-headed bunting Reproduction & Black-headed bunting Diet for Black-headed bunting Behavior of the Bird
Black-headed bunting Scientific Classification
Domain:
Kingdom: Eukaryota
Phylum: Animalia
Class: Chordata
Order: Aves
Family: Passeriformes
Genus:
Species:
Data Source: Wikipedia.org
Black-headed bunting Characteristics
The Black-headed bunting is a small bird with a striking black head and white throat. It is commonly found in grasslands and open areas across Europe and Asia. This bird is known for its beautiful song, which it uses to attract mates and defend its territory. The Black-headed bunting feeds on insects and seeds, and can often be seen hopping around on the ground in search of food. Despite its small size, this bird is a tough survivor, able to withstand harsh weather conditions and predators.
Black-headed bunting Lifespan
The average lifespan of a Black-headed bunting is around 2-3 years. However, some individuals can live up to 5 years in the wild. This bird species faces threats such as habitat loss and predation, which can impact their longevity.
Black-headed bunting Diet
The Black-headed bunting’s diet mainly consists of insects, seeds, and small fruits. They use their sharp beaks to catch insects in flight and also forage on the ground for seeds and fruits. They have a varied diet to ensure they get all the nutrients they need.
Black-headed bunting Behavior
The Black-headed bunting is a bird that is known for its vibrant plumage and cheerful chirping. They are social creatures, often seen foraging for food in groups.
Black-headed bunting Reproduction
Black-headed buntings reproduce by laying eggs in a nest made of twigs and grass. The female bird incubates the eggs until they hatch, and both parents care for the chicks.
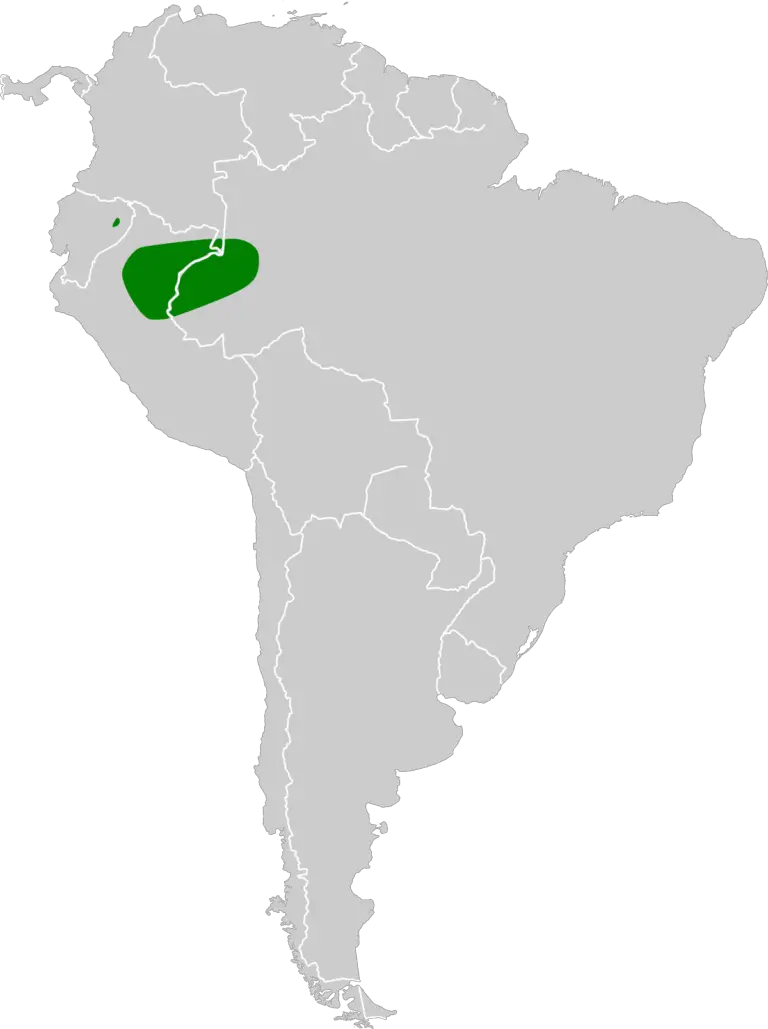
Black-headed bunting Location and Habitat
The Black-headed bunting is commonly found in grasslands, meadows, and farmlands across Europe and Asia. They prefer open areas with low vegetation where they can easily forage for insects and seeds.
Black-headed bunting Conservation Status
The Black-headed bunting is classified as “Least Concern” on the conservation status scale, meaning it is not currently at risk of extinction.
Black-headed bunting Predators
Black-headed buntings face threats from predators like snakes, birds of prey, and mammals. These predators hunt the small birds for food, posing a constant danger to their survival.
Black-headed bunting FAQs
- What is a Black-headed bunting?
A Black-headed bunting is a small bird species known for its distinctive black head and white body. - Where can Black-headed buntings be found?
Black-headed buntings can be found in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. - What do Black-headed buntings eat?
Black-headed buntings primarily feed on seeds, insects, and small fruits. - Are Black-headed buntings migratory birds?
Yes, Black-headed buntings are migratory birds that typically travel south for the winter months. - How can I identify a Black-headed bunting?
You can identify a Black-headed bunting by its black head, white body, and brown wings. - What is the breeding season for Black-headed buntings?
The breeding season for Black-headed buntings typically begins in late spring and lasts through the summer months. - Do Black-headed buntings build nests?
Yes, Black-headed buntings build cup-shaped nests in shrubs or trees using grass, twigs, and feathers. - Are Black-headed buntings considered endangered?
No, Black-headed buntings are not considered endangered and are listed as a species of Least Concern by the IUCN. - How long do Black-headed buntings live?
Black-headed buntings have an average lifespan of around 3-5 years in the wild. - Do Black-headed buntings have any predators?
Black-headed buntings are preyed upon by birds of prey, snakes, and mammals such as cats and foxes.