Blue-rumped parrot
“The vibrant colors of the Blue-rumped parrot light up the sky with beauty and grace.”
Best Quotes for Blue-rumped parrot Bird
Blue-rumped parrot Lifespan related to Blue-rumped parrot Predators & Blue-rumped parrot Conservation Status also Blue-rumped parrot Location and Habitat important regarding Blue-rumped parrot Reproduction & Blue-rumped parrot Diet for Blue-rumped parrot Behavior of the Bird
Blue-rumped parrot Scientific Classification
Domain: Chordata
Kingdom: Aves
Phylum: Psittaciformes
Class: Psittaculidae
Order: Psittinus
Family:
Genus:
Species:
Data Source: Wikipedia.org
Blue-rumped parrot Characteristics
The Blue-rumped parrot is a small, colorful bird native to Southeast Asia. It has a bright blue patch on its lower back, giving it its name. These parrots are social creatures that live in small flocks and communicate with a variety of calls and squawks. They primarily feed on fruits, seeds, and insects. The Blue-rumped parrot is known for its playful and curious nature, making it a popular choice as a pet bird. However, they are also threatened by habitat loss and illegal trapping for the pet trade, leading to a decline in their population numbers.
Blue-rumped parrot Lifespan
The Blue-rumped parrot has a lifespan of approximately 20-30 years in the wild. However, in captivity, they can live up to 40 years or even longer with proper care and nutrition. This means that they can be a long-term companion for those who choose to have them as pets.
Blue-rumped parrot Diet
The Blue-rumped parrot mainly eats fruits, seeds, nuts, and flowers. They also enjoy some insects and small invertebrates. It is important for them to have a varied diet to stay healthy and strong.
Blue-rumped parrot Behavior
The Blue-rumped parrot is known for its playful and social behavior. It loves to interact with other birds and enjoys flying and exploring its surroundings.
Blue-rumped parrot Reproduction
Blue-rumped parrots reproduce by laying eggs, with the female typically laying 3-4 eggs in a clutch. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs until they hatch.
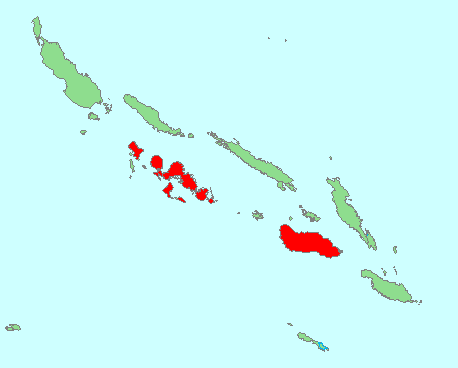
Blue-rumped parrot Location and Habitat
The Blue-rumped parrot is found in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, including countries like Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand. They prefer to live in areas with dense vegetation and plenty of fruit trees.
Blue-rumped parrot Conservation Status
The Blue-rumped parrot is classified as near threatened due to habitat loss and illegal trapping for the pet trade. Conservation efforts are needed to protect this species.
Blue-rumped parrot Predators
The predators of the Blue-rumped parrot include snakes, birds of prey, and feral cats. They hunt the parrots for food, posing a threat to their survival.
Blue-rumped parrot FAQs
- What is a Blue-rumped parrot?
The Blue-rumped parrot is a small species of parrot native to Southeast Asia. - What does a Blue-rumped parrot look like?
They have a predominantly green body with a blue patch on their rump and yellow markings on their wings. - How big do Blue-rumped parrots get?
They typically grow to be around 10 inches in length. - What do Blue-rumped parrots eat?
They primarily feed on fruits, seeds, nuts, and flowers. - Are Blue-rumped parrots good pets?
Blue-rumped parrots can make good pets for experienced bird owners, as they require a lot of socialization and mental stimulation. - Do Blue-rumped parrots mimic human speech?
While they are not known for their ability to mimic human speech as well as some other parrot species, they can still learn a few words and sounds. - How long do Blue-rumped parrots live?
Blue-rumped parrots have a lifespan of around 15-20 years in captivity. - Are Blue-rumped parrots endangered?
Yes, Blue-rumped parrots are considered near threatened in the wild due to habitat loss and illegal trapping for the pet trade. - Do Blue-rumped parrots need a large cage?
Yes, Blue-rumped parrots require a spacious cage with plenty of room for flying and playing. - Can Blue-rumped parrots be kept in pairs?
Blue-rumped parrots are social birds and do well when kept in pairs or small groups, as long as they are properly introduced and have enough space.