Bornean whistler
“The Bornean whistler’s melodic tunes fill the jungle with joy.”
Best Quotes for Bornean whistler Bird
Bornean whistler Lifespan related to Bornean whistler Predators & Bornean whistler Conservation Status also Bornean whistler Location and Habitat important regarding Bornean whistler Reproduction & Bornean whistler Diet for Bornean whistler Behavior of the Bird
Bornean whistler Scientific Classification
Domain: Chordata
Kingdom: Aves
Phylum: Passeriformes
Class: Pachycephalidae
Order: Pachycephala
Family:
Genus:
Species:
Data Source: Wikipedia.org
Bornean whistler Characteristics
The Bornean whistler is a small bird found in the rainforests of Borneo. It is known for its beautiful whistling calls that can be heard echoing through the trees. This bird has a distinctive black and white plumage with a bright red eye. The Bornean whistler feeds on insects and small fruits, using its sharp beak to catch prey. It is a secretive bird that is often hard to spot due to its camouflage and shy nature. Despite its small size, the Bornean whistler plays an important role in the ecosystem by helping to control insect populations.
Bornean whistler Lifespan
The Bornean whistler, a small bird found in Borneo, typically lives for about 6 to 10 years in the wild. However, some individuals have been known to live up to 15 years. These birds face threats such as habitat loss and deforestation, which can impact their lifespan.
Bornean whistler Diet
The Bornean whistler eats insects, fruits, and small animals. It catches bugs by flying out from its perch and snatching them in mid-air. It also feeds on berries and seeds found in the forest.
Bornean whistler Behavior
The Bornean whistler is a shy bird that communicates through high-pitched whistles. It is often seen perched high in trees, feeding on insects and fruits.
Bornean whistler Reproduction
Bornean whistlers reproduce by laying eggs in nests built by the female. The male helps in feeding and protecting the chicks until they are old enough to fly.
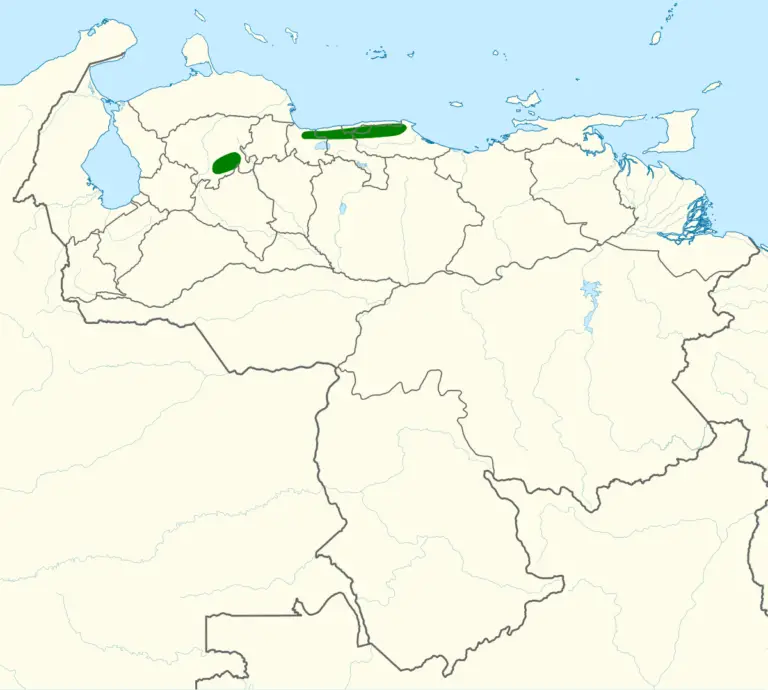
Bornean whistler Location and Habitat
The Bornean whistler can be found in the dense forests of Borneo, an island in Southeast Asia known for its rich biodiversity. These small birds are often heard singing melodious tunes in the treetops.
Bornean whistler Conservation Status
The Bornean whistler is classified as a species of least concern, meaning its population is stable and not at risk of extinction.
Bornean whistler Predators
The predators of the Bornean whistler include snakes, birds of prey, and small mammals. They hunt the whistler for food, posing a threat to its survival.
Bornean whistler FAQs
- What is a Bornean whistler?
A Bornean whistler is a small bird species native to the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. - What does a Bornean whistler look like?
Bornean whistlers have a distinctive black and white plumage with a yellow patch on their wings. - What do Bornean whistlers eat?
Bornean whistlers primarily feed on insects and small invertebrates found in the forest canopy. - Where can Bornean whistlers be found?
Bornean whistlers are commonly found in the forests of Borneo, particularly in lowland and montane areas. - Are Bornean whistlers endangered?
Yes, Bornean whistlers are considered near-threatened due to habitat loss and fragmentation caused by deforestation. - How do Bornean whistlers communicate?
Bornean whistlers are known for their melodious whistling calls that they use to communicate with other members of their species. - Do Bornean whistlers migrate?
Bornean whistlers are non-migratory birds and tend to stay in their preferred forest habitats year-round. - How do Bornean whistlers build their nests?
Bornean whistlers build cup-shaped nests made of twigs, moss, and leaves in the branches of trees. - How many eggs do Bornean whistlers typically lay?
Bornean whistlers usually lay 2-3 eggs per clutch, which are incubated by the female for about two weeks. - How can I help protect Bornean whistlers?
You can help protect Bornean whistlers by supporting conservation efforts, reducing deforestation, and promoting sustainable land use practices in their habitats.