Black-backed forktail
“The Black-backed forktail dazzles with its distinctive beauty and grace.”
Best Quotes for Black-backed forktail Bird
Black-backed forktail Lifespan related to Black-backed forktail Predators & Black-backed forktail Conservation Status also Black-backed forktail Location and Habitat important regarding Black-backed forktail Reproduction & Black-backed forktail Diet for Black-backed forktail Behavior of the Bird
Black-backed forktail Scientific Classification
Domain: Chordata
Kingdom: Aves
Phylum: Passeriformes
Class: Muscicapidae
Order: Enicurus
Family:
Genus:
Species:
Data Source: Wikipedia.org
Black-backed forktail Characteristics
The Black-backed forktail is a small bird found in Asia. It has a black back and white belly, with a distinctive tail that helps it balance on narrow branches. These birds are commonly found near streams and rivers, where they feed on insects and small fish. They are known for their agile flying and ability to catch prey in mid-air. The Black-backed forktail is an important part of the ecosystem, helping to control insect populations and serving as a food source for larger predators.
Black-backed forktail Lifespan
The Black-backed forktail, a small bird found in Asia, has a lifespan of around 3 to 5 years in the wild. However, in captivity, they can live up to 10 years. These birds are known for their distinctive black and white coloring and can be found near streams and rivers.
Black-backed forktail Diet
The Black-backed forktail eats insects like beetles, caterpillars, and ants. It also feeds on small fish and tadpoles. They catch their prey by diving into water or hopping along the ground.
Black-backed forktail Behavior
Black-backed forktails are shy birds that stick close to water sources. They have a unique habit of flicking their tails up and down while perched on a branch.
Black-backed forktail Reproduction
Black-backed forktails reproduce by laying eggs in nests near streams. The female incubates the eggs while the male hunts for food. The chicks hatch and are cared for by both parents.
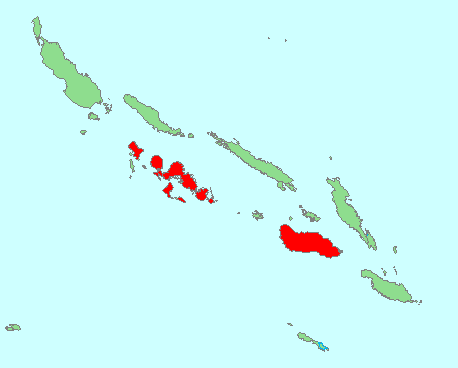
Black-backed forktail Location and Habitat
The Black-backed forktail can be found near fast-flowing streams and rivers in forested areas. Look for this small bird with a black back and white belly flitting around the water.
Black-backed forktail Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Black-backed forktail is classified as Least Concern, meaning the species is not currently at risk of extinction.
Black-backed forktail Predators
Black-backed forktails are hunted by snakes, birds of prey, and larger mammals. These predators rely on stealth and speed to catch the small, elusive birds for food.
Black-backed forktail FAQs
- What is a Black-backed forktail?
A Black-backed forktail is a small bird species found in Asia. - What do Black-backed forktails eat?
Black-backed forktails primarily feed on insects and small aquatic organisms. - Where do Black-backed forktails live?
Black-backed forktails are commonly found near fast-flowing streams and rivers in wooded areas. - How can I identify a Black-backed forktail?
Black-backed forktails have a distinctive black back and tail, with a white belly and throat. - Are Black-backed forktails migratory birds?
No, Black-backed forktails are resident birds and do not migrate. - Do Black-backed forktails build nests?
Yes, Black-backed forktails build cup-shaped nests made of moss, leaves, and twigs near water bodies. - Are Black-backed forktails endangered?
No, Black-backed forktails are not considered endangered and are fairly common in their habitat. - How do Black-backed forktails communicate?
Black-backed forktails communicate through various vocalizations, including chirps and trills. - Do Black-backed forktails have predators?
Yes, predators of Black-backed forktails include larger birds of prey and snakes. - How can I attract Black-backed forktails to my garden?
You can attract Black-backed forktails to your garden by providing a clean water source and planting native vegetation that attracts insects.